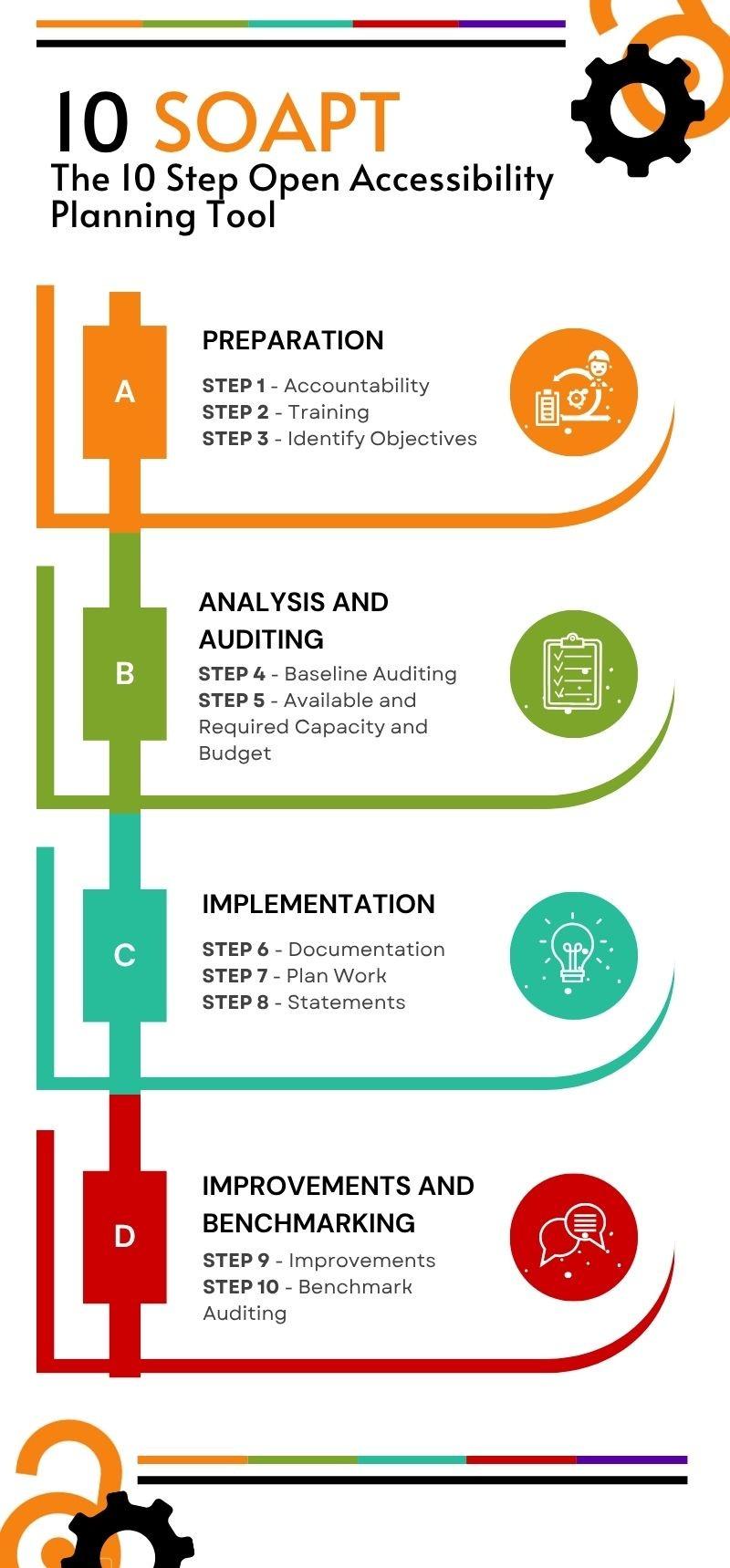
Our Planning Tool - 10 SOAPT
The 10 Step Open Accessibility Planning Tool
Our custom planning tool has been developed by Open Book Futures to help small presses achieve accessibility across their organisation. It consists of 10 steps organised into 4 sections A-D. For each step, we have developed guidance that is hosted here on our Copim Compass area that will help you understand it fully. Our guidance is organised into 5 areas: Plan, Check, Learn, Communicate and Evidence, and we link to the exact areas of each of those that are relevant to each of the 10 steps below.
Each of the 10 steps are given a list of tasks, with each task given a label of mandatory and optional. For this reason, the model is presented twice below - once in chronological order, and then again split by mandatory or optional tasks.
You can use the model as a self assessment tool, by giving each of the tasks a grading as below:
0 - Unaware
1 - Aware but not actioned
2 - Trying to action but some barriers
3 - Starting to action
4 - In the middle of actioning
5 - Actioned and achieved
And you can return to this self assessment at multiple points in your journey. We suggested assessing your Current Level, Desired Level and Achieved Level (after some improvements are made).
You can also access 10 SOAPT formatted as a spreadsheet: 10 SOAPT [Google Sheets]
View this information as a video
10 SOAPT
Section A Preparation
Step 1 Accountability
Appoint a person to co-ordinate accessibility, who could be a dedicated accessibility professional or someone who has a wider portfolio of work that includes accessibility too. However, it's also important to remember that some accessibility work will be completed by almost everyone at an organisation.
Task A. Appoint a person to co-ordinate accessibility (recommended)
Task B. Ensure the whole press is aware they need to engage with accessibility tasks (recommended)
Task C. Consider external certification services (optional)
Step 2 Training
Plan technical digital accessibility training and support the identified staff to develop skills. See our Courses and Training Materials and Guidance pages. You can also look up a summary of your country's legislation and learn more about available standards in our section Learn.
Task A. Identify sources of suitable accessibility training (recommended)
Task B. Consider custom paid for accessibility training (optional)
Task C. Support the identified accessibility co-ordinator to develop skills (recommended)
Step 3 Identify Objectives
Once relevant staff have been identified and trained, some organisational accessibility objectives can be devised through requirements gathering exercises. Any organisation should aim to meet legal minimum requirements, but it's possible to be exempt from that (this requires work to evidence), and you may decide to go beyond in some areas if it fits with your organisational values. Also, your readership might already have made accessibility requests you haven't been able to meet yet, or you could survey your end users to capture this 'reader voice' in terms of accessibility requirements. Finally, it's possible there are some community or discipline specific considerations to include as well.
Task A. Consider applicability of legislation and whether the press is exempt (if so, plan to evidence this) (recommended)
Task B. Complete requirements gathering from readership (optional)
Task C. Capture community / discipline specific considerations (optional)
Task D. Consider where you might decide to go beyond legal minimum (parts of WCAG AAA or other accessibility features requested by readership or research discipline) (optional)
Section B Analysis and Auditing
Step 4 Baseline Auditing
Audit the current accessibility of all aspects of the organisation, including the frontlist and backlist book files, the website functionality and the backend submission platform. You could complete this yourself using self auditing, or employ an external auditor. You could also look at assessing current organisational knowledge, attitudes towards and motivations for engaging with accessibility work. You can find our overall guidance on auditing, including our custom Checklist OARC here: Check.
Task A. Consider capturing current organisational knowledge, attitudes towards and motivations for engaging with accessibility work (optional)
Task B. Complete Automated Testing (recommended)
Task C. Complete Manual Testing (recommended)
Task D. Complete Assistive Technology Tests (optional)
Task E. Complete End User Testing from Print Disabled People (optional)
Task F. Consider external auditing services (optional)
Step 5 Available and Required Capacity and Budget
Improving accessibility requires dedicated time and money, and a full consideration of where this can be diverted to accessibility goals will help with planning. It is likely that you will have some idea of how long book production tasks take, and how much extra work accessibility improvements will add to that, but it could be that you will need to understand more about the relative simplicity or complexity of individual accessibility requirements (like ALT text, or checking colour contrast). You can see our estimation of this within our custom Checklist tool OARC here: The Open Accessibility Review Checker (OARC).
Task A. Frontlist: Use checklist with complexity and current knowledge of workflows to estimate time required to complete accessibility tasks (recommended)
Task B. Backlist: Use checklist with complexity and current knowledge of workflows to estimate time required to complete accessibility tasks (recommended)
Task C. Plan and assign budget (recommended)
Section C Implementation
Step 6 Documentation
Capturing the results of identifying objectives, auditing, and analysing resources might happen across a range of documentation that could include: an accessibility policy, roadmaps, strategic plans, updated author guidelines, or other documentation. We offer guidance on producing documentation in our sections on Author Guidelines and Accessibility Policy.
Task A. Plan documentation that could include: an accessibility policy, roadmaps, strategic plans, updated author guidelines, or other documentation (recommended)
Task B. Create an Accessibility Policy (optional)
Task C. Update Author Guidelines to include accessibility tasks (mandatory)
Step 7 Plan Work
We recommend that frontlist and backlist/remediation are considered separately, and separate plans are made for the website including the backend submission process.
Task A. Front list / Born Accessible - Create accessible book files (recommended)
Task B. Back list / Remediation - Upgrade the accessibility of existing book files (recommended)
Task C. The Website functionality - Improve accessibility of HTML books and whole website (recommended)
Step 8 Statements
Publish accessibility statements and roadmaps on the organisation's website, and include VPATs and public policies if that is decided on. Our guidance on each is available at the links.
Task A. Create an Accessibility Statement on a public web page (recommended)
Task B. Update your initial VPAT (optional)
Task C. Consider sharing the Accessibility Policy openly, if decided on (optional)
Section D Improvements and Benchmarking
Step 9 Improvements
Incorporate planned accessibility improvements into workflows and complete the plan.
Task A. Complete the plan (recommended)
Step 10 Benchmark Auditing
Audit the accessibility and organisational knowledge at regular intervals within the plan to showcase improvements.
Task A. Audit again at regular intervals (recommended)
SOAPT by recommended/optional tasks
Recommended
Task 1A. Appoint a person to co-ordinate accessibility
Task 1B. Ensure the whole press is aware they need to engage with accessibility tasks
Task 2A. Identify sources of suitable accessibility training
Task 2C. Support the identified accessibility co-ordinator to develop skills
Task 3A. Consider applicability of legislation and whether the press is exempt (if so, plan to evidence this)
Task 4B. Complete Automated Testing
Task 4C. Complete Manual Testing
Task 5A. Frontlist: Use checklist with complexity and current knowledge of workflows to estimate time required to complete accessibility tasks
Task 5B. Backlist: Use checklist with complexity and current knowledge of workflows to estimate time required to complete accessibility tasks
Task 5C. Plan and assign budget
Task 6A. Plan documentation that could include: an accessibility policy, roadmaps, strategic plans, updated author guidelines, or other documentation
Task 6C. Update Author Guidelines to include accessibility tasks
Task 7A. Front list / Born Accessible - Create accessible book files
Task 7B. Back list / Remediation - Upgrade the accessibility of existing book files
Task 7C. The Website functionality - Improve accessibility of HTML books and whole website
Task 8A. Create an Accessibility Statement on a public web page
Task 9A. Complete the plan
Task 10A. Audit again at regular intervals
Optional
Task 1C. Consider external certification services
Task 2B. Consider custom paid for accessibility training
Task 3B. Complete requirements gathering from readership
Task 3C. Capture community / discipline specific considerations
Task 3D. Consider where you might decide to go beyond legal minimum (parts of WCAG AAA or other accessibility features requested by readership or research discipline)
Task 4A. Consider capturing current organisational knowledge, attitudes towards and motivations for engaging with accessibility work
Task 4D. Complete Assistive Technology Tests
Task 4E. Complete End User Testing from Print Disabled People
Task 4F. Consider external auditing services
Task 6B. Create an Accessibility Policy
Task 8B. Update your initial VPAT
Task 8C. Consider sharing the Accessibility Policy openly, if decided on


No comments to display
No comments to display